|
Did you know?
The MEG brain scan images the brain by detecting the magnetic fields
caused by electrical pulses along nerves and across neurons in the brain. These fields are
very weak and require extremely sensitive instruments called SQUIDs (superconducting quantum
interference devices) to measure them.
10
|
A magnetic field is a force field with which moving electric charges, or any changing electric field, and magnetically polarized materials interact. Particle accelerators do not typically use magnetically polarized material, so this topic will not be explained in detail. Suffice it to say that a polarized material is one that holds a magnetic field and thus generates a magnetic field in the surrounding space. For those interested, here is a more detailed explanation of magnetic polarization.
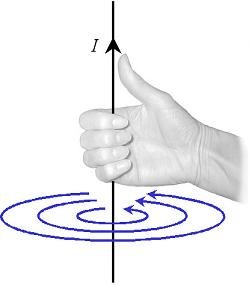
A moving electric charge also interacts via magnetic field. A moving charge will result in a changing electric field, which generates a magnetic field. This leads to the fact that a series of moving charges, or an electric current, will generate a magnetic field. The field B generated by a current I is given by the Biot-Savart Law.1
As such, a current through a loop will generate a magnetic field. This means that the magnetic field in the centre of the loop will be perpendicular to the loop, or along the axis of the loop. The direction of the magnetic field along this axis is determined by the direction of the current around the loop in accordance with the right hand rule.
By superimposing the fields from two such loops parallel to one another, a magnetic field that is approximately uniform along a vector perpendicular to the area of the loops can be obtained. More detail of this superposition can be found here. his field is also approximately uniform at small radius from the axis through the centre of both loops. This is how electromagnets are made.
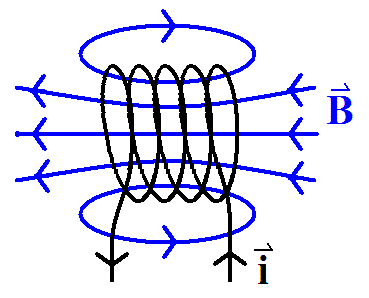
Magnetic Field cause by a current through a coil