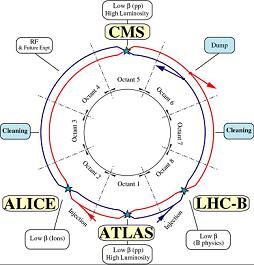
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the largest circular particle accelerator in the world. The collider is contained in a tunnel, 50m to 175m in depth. With a precise circumference of 26,659m, it is the largest particle accelerator in the world. The LHC holds the potential of accelerating two 7 TeV beams of protons into a corresponding 14 TeV head to head collision at a rate of 600 million collisions per second. That's equivalent to a power of 1345 Watts! Construction on the LHC began in the 1980s; it had a successful run in September of 2008, but due to some faults it is not expected to be running again until September 2009. 20
The LHC is equipped with different accelerators and detectors that work to serve various purposes. First, protons are accelerated by the linear particle accelerator, LINAC 2, generating 0.12 GeV protons. These then enter the Proton Synchrotron Booster (PSB). There the protons are accelerated to 1.4 GeV and injected into the Proton Synchrotron (PS), where they are accelerated to 26 GeV. The last step before being injected into the main synchrotron is the Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) is used to further increase their energy to 450 GeV. Finally they are injected into the main ring, where it takes 20 minutes to accelerate the protons to 7TeV. They will continue to circulate for 10 to 24 hours while collisions occur and are recorded with the detectors. 21
There are six detectors at the LHC, two of which are general detectors, while the others
serve more specific purposes. The general detectors, ATLAS (A Toroidal LHC ApparatuS) and
CMS (Compact Muon Solenoid) will search for "new physics," including evidence of the Higgs
Boson, and dark matter. The more specific detectors are ALICE (A Large Ion Collider
Experiment, which will study quark-gluon plasma), LHCb (Large Hadron Collider beauty, which
will seach for evidence of antimatter, that is the beauty or bottom quark), LHCf (Large
Hadron Collider forward, which is to study what happens in front of the colliding beams) and
TOTEM (Total Cross Section, Elastic Scattering and Diffraction Dissociation- and those are
exactly what it is supposed to measure).
22
Then you can check out this video for more detail:
And if you're interested in learning more about the detectors at the LHC, check this out.